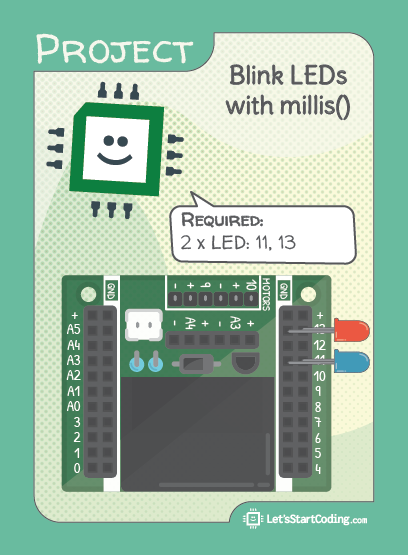
Blink LEDs with millis()
Step 1 - Build the Project
This code avoids delays and instead uses a timer built into the Arduino software called millis(). Millis() starts running when a program starts and continues to count up every millisecond the program is running. Here you make use of it by comparing a variable to the millis() count.
Step 2 - Upload the Code
Step 3 - Read the Walkthrough
The first check in the code is “Is millis() - 0 > 3500?”. This is asking, in effect, “Has it been more than 3.5 seconds since the top of the loop?”. If it has, then you want to run the code inside the loop. Otherwise, the code moves on.
We can’t change the value of millis(), but we can control the value of the variables. Within each ‘if’ loop, you reset the timers to the value of millis() (which is always streaming upward). Because the values are equal, the difference if you subtract them from each other is 0. Millis() will continue to rise, however, while the variable keeps its value until you update it again.
Continually checking this timer can be tricky, but it allows you to control one process while another keeps occurring in the background.